ETF
An ETF is an exchange-traded index fund that tracks the performance of an index, such as the S&P 500. In essence, ETFs combine the advantages of stocks and funds in one product.
Key points
- ETF's (Exchange Traded Funds) are exchange traded index funds.
- Investing in ETFs is (mostly) a passive investment approach
- ETFs save costs compared to "active funds
ETF Definition: Exchange Traded Funds - exchange traded index funds
ETF's allow you to invest in entire markets with one security at a low cost. For example, with a single MSCI World ETF you spread your investment over around 1,600 companies from all over the world. In addition to equities, ETFs also allow you to invest in many other asset classes. Because of this diversity and their specific characteristics, ETFs are perfect building blocks for private investment. So, it's no wonder that more and more investors are turning to ETFs for wealth creation. ETFs simply replicate a market index one-to-one and - like a share - can be traded on the stock exchange at any time.
An ETF is an exchange-traded index fund.
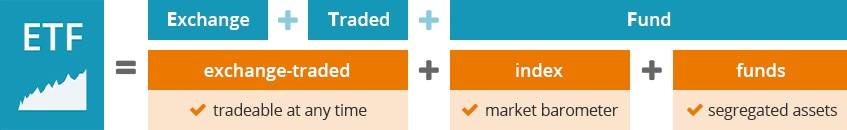
The best way to explain how an ETF works and its benefits is to look at the three parts that make up the term "exchange-traded index fund."
What is a mutual fund?
A mutual fund is a collection point for investment money. In simple terms, many investors pool their money and give a professional (fund manager) the task of investing the capital as profitably and widely as possible within the framework of a specified investment strategy.
How an investment fund works

The investment strategy specifies the asset classes (for example, stocks, bonds, and commodities) in which the fund manager may invest.
The special feature of an investment fund is that the money of the investors is a special asset, which is held in trust by a custodian bank and is legally separate from the assets of the fund company. Therefore, the invested money is protected even in the event of insolvency of the fund company.
The manager of a traditional fund has the task of achieving a higher return than that of the respective comparative index (benchmark) by buying and selling securities. However, according to scientific studies, only very few fund managers succeed in doing this over the long term (for example, over a period of more than three years).
Index funds - what are they?
In an index fund, the provider ensures that the fund tracks the performance of an index as closely as possible. The securities contained in the fund and their weighting are therefore precisely specified by the index being tracked. Indices are market barometers that make it possible to track the performance of entire markets.
An index fund has the great advantage that YOU always know what you are invested in. Because the composition of the underlying index, such as the S&P 500, is known and can be viewed at any time. The Standard & Poor's 500 Index (S&P 500) contains e.g. shares of the 500 largest US companies.
Due to the index replication, index funds/ETFs (compared to active investment funds) do not require extensive analyses for stock selection. For this reason, the ETF provider receives only a very small annual fee for its services. ETFs are therefore also significantly cheaper than classic mutual funds - and in most cases show better performance.
Exchange-traded index funds - What does that mean?
Just like stocks, ETFs are traded on the stock exchange. Therefore, you can buy and sell ETFs at any time during stock exchange opening hours. In comparison, classic funds are only traded once a day through the fund company.
While classic funds usually have high issue surcharges, ETFs are only traded on the stock exchange for the bank's order fees and a usually small difference between the buying and selling price ("spread").
Conclusion
ETFs - Exchange Traded Funds - function in a similar way to traditional funds: they can be traded on the stock exchange like shares and track a securities index. In most cases, ETFs are passively managed index funds. Anyone looking for a low-cost, flexible, and simple way to build up assets will find what they are looking for here.